Navigating the Korean Peninsula: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of South Korea
Related Articles: Navigating the Korean Peninsula: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of South Korea
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Korean Peninsula: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of South Korea. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Korean Peninsula: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of South Korea
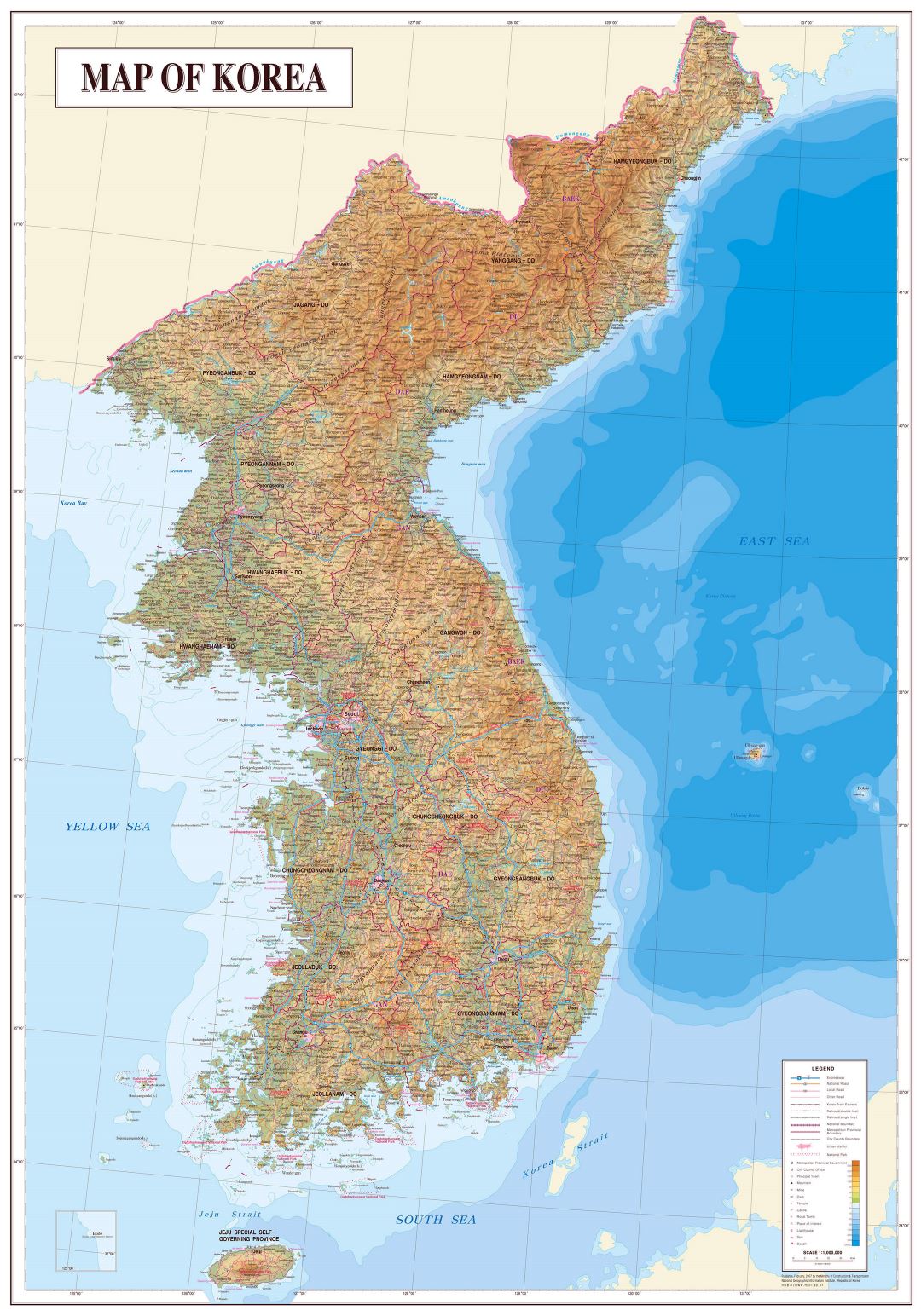
The Korean Peninsula, a landmass jutting out from the Asian mainland, is home to a rich history, vibrant culture, and a complex geopolitical landscape. Understanding the geography of South Korea, specifically, is essential for appreciating its unique identity and its place in the world. This comprehensive guide delves into the physical characteristics, political divisions, and key regions of South Korea, offering a nuanced perspective on its geographic significance.
Physical Geography: A Land of Mountains and Coastlines
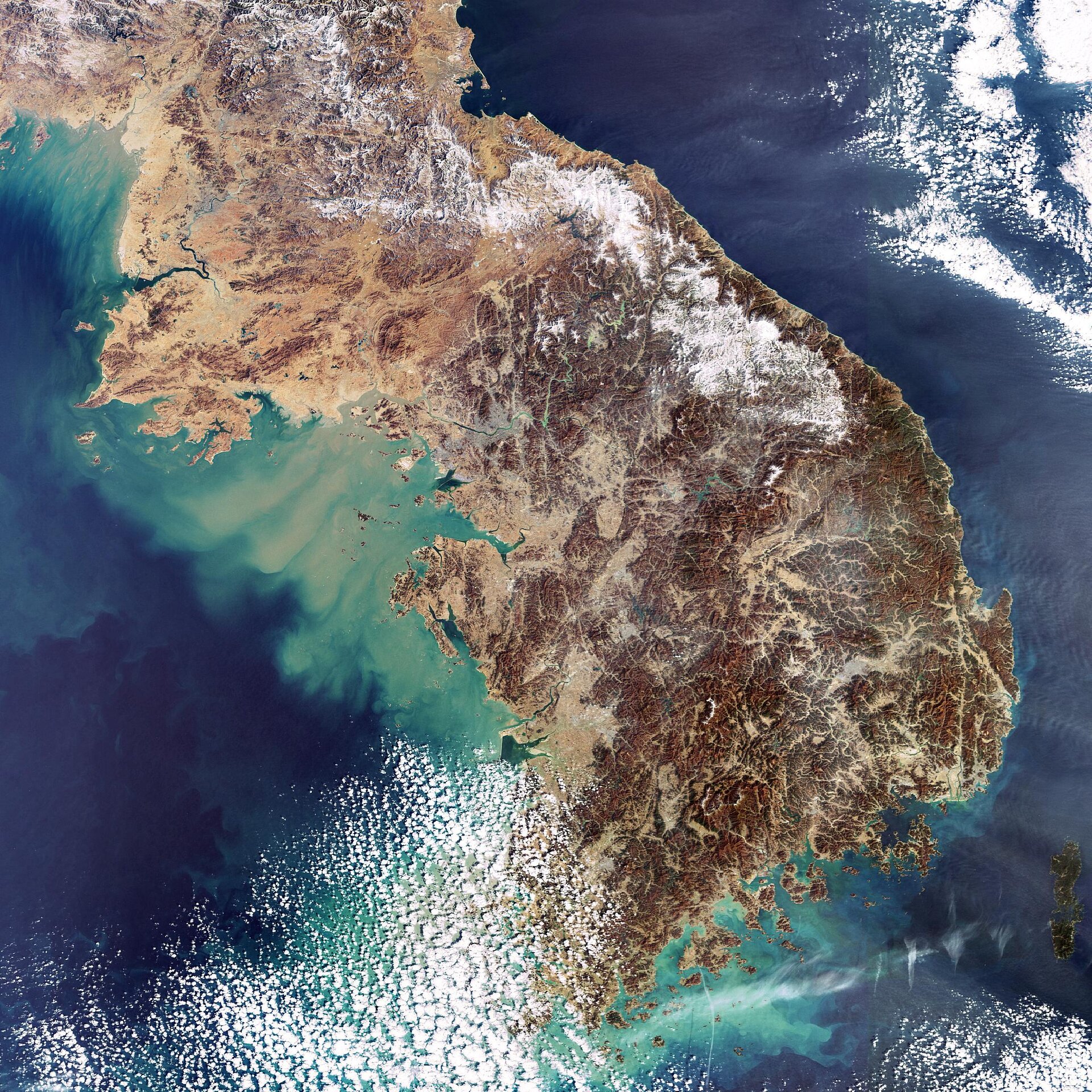
South Korea’s landscape is characterized by its mountainous terrain, with over 70% of the country covered by hills and mountains. The Taebaek Mountains, running along the eastern edge, form a natural barrier, influencing weather patterns and shaping the distribution of population. The peninsula’s western and southern coasts are dotted with numerous islands and inlets, offering a diverse coastline that has played a significant role in its history and economy.
The Importance of Mountains:
The Taebaek Mountains, with their rugged peaks and deep valleys, have long served as a natural defense against invaders, contributing to the development of distinct regional identities. The mountains also play a crucial role in South Korea’s water resources, serving as the source of major rivers like the Han River, which flows through Seoul and provides water for a significant portion of the population.
Coastal Diversity:
South Korea’s coastline, stretching over 2,400 kilometers, is characterized by its diverse features, ranging from sandy beaches and rocky cliffs to tidal flats and estuaries. These varied coastal environments have supported a thriving fishing industry and facilitated trade with neighboring countries. The southern coast, in particular, is known for its numerous islands, including Jeju Island, a popular tourist destination renowned for its volcanic landscape and subtropical climate.
Political Divisions: From North to South
The Korean Peninsula is divided into two distinct entities: North Korea and South Korea. The division, a result of the Korean War (1950-1953), has created a unique geopolitical situation, with a heavily militarized border known as the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) separating the two nations.
The DMZ: A Symbol of Division and Hope
The DMZ, despite its name, is one of the most heavily fortified borders in the world. It serves as a physical reminder of the division of the Korean Peninsula and the ongoing tension between the two Koreas. However, the DMZ also represents a potential for reunification and a symbol of hope for a peaceful future.
Regional Identities: A Mosaic of Cultural Diversity
South Korea is further divided into eight provinces, each with its own unique history, culture, and traditions. These regions, ranging from the bustling metropolitan areas of Seoul and Busan to the mountainous landscapes of Gangwon and North Jeolla, contribute to the rich tapestry of Korean culture.
Seoul: The Heart of South Korea
Seoul, the capital and largest city, is a vibrant metropolis that embodies the dynamism of modern South Korea. It is a center of finance, technology, and culture, attracting people from all corners of the country and the world.
Busan: A Coastal City with a Maritime Heritage
Busan, located on the southeastern coast, is South Korea’s second-largest city and a major port city. It is renowned for its seafood, beaches, and vibrant nightlife. Busan’s maritime heritage is evident in its historical fishing villages and its role as a key hub for international trade.
Jeolla Provinces: A Land of Food and Culture
The Jeolla Provinces, located in the southwestern region, are known for their rich agricultural land and their traditional cuisine. The region is famous for its spicy kimchi, fermented soybean paste (doenjang), and various seafood dishes.
Gangwon Province: A Mountainous Paradise
Gangwon Province, located in the eastern part of the country, is dominated by the Taebaek Mountains. It is a popular destination for hiking, skiing, and other outdoor activities. The province is also home to the DMZ, offering a unique perspective on the history and current state of the Korean Peninsula.
Understanding the Geographic Significance
South Korea’s geography has shaped its history, culture, and economy in profound ways. The mountainous terrain, the diverse coastline, and the political division have all played a significant role in shaping the country’s identity and its place in the world.
Economic Development: A Balancing Act
South Korea’s economic development has been heavily influenced by its geography. The mountainous terrain has presented challenges for infrastructure development, while the coastline has facilitated trade and economic growth. The country’s reliance on imports for resources has also been a factor in its economic policies.
Cultural Identity: A Blend of Tradition and Modernity
South Korea’s geography has also played a role in shaping its cultural identity. The mountainous terrain has fostered a sense of regionalism, with distinct dialects and traditions developing in different parts of the country. The coastline has also influenced Korean cuisine, with seafood playing a prominent role in many traditional dishes.
Geopolitical Significance: A Crossroads of Power
South Korea’s location on the Korean Peninsula, a strategically important region in East Asia, has placed it at the crossroads of major powers. The country’s close relationship with the United States, its economic ties with China, and its complicated relationship with North Korea have all shaped its geopolitical landscape.
FAQs about South Korea’s Geography
Q: What is the highest mountain in South Korea?
A: Mount Hallasan, located on Jeju Island, is the highest mountain in South Korea, reaching a height of 1,950 meters.
Q: What is the largest island in South Korea?
A: Jeju Island, located off the southern coast, is the largest island in South Korea, with an area of 1,846 square kilometers.
Q: What are the main rivers in South Korea?
A: The main rivers in South Korea include the Han River, the Nakdong River, and the Geum River.
Q: What is the climate like in South Korea?
A: South Korea has a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. Summers are hot and humid, while winters are cold and dry.
Q: What are some of the major cities in South Korea?
A: Some of the major cities in South Korea include Seoul, Busan, Daegu, Incheon, Gwangju, and Daejeon.
Tips for Exploring South Korea’s Geography
1. Visit the DMZ: A visit to the DMZ offers a unique perspective on the history and current state of the Korean Peninsula.
2. Hike in the Taebaek Mountains: The Taebaek Mountains offer stunning scenery and a chance to experience the natural beauty of South Korea.
3. Explore the Jeolla Provinces: The Jeolla Provinces are known for their rich agricultural land and their traditional cuisine.
4. Visit Jeju Island: Jeju Island is a popular tourist destination known for its volcanic landscape and subtropical climate.
5. Learn about Korean history and culture: Understanding Korean history and culture will enhance your appreciation of the country’s geography and its people.
Conclusion: A Land of Contrasts and Opportunities
South Korea, with its diverse geography, rich history, and dynamic culture, is a fascinating country to explore. From its towering mountains to its vibrant cities, from its ancient traditions to its modern innovations, South Korea offers a unique and rewarding experience for visitors and residents alike. Understanding the country’s geography is essential for appreciating its complexities and its potential for the future.
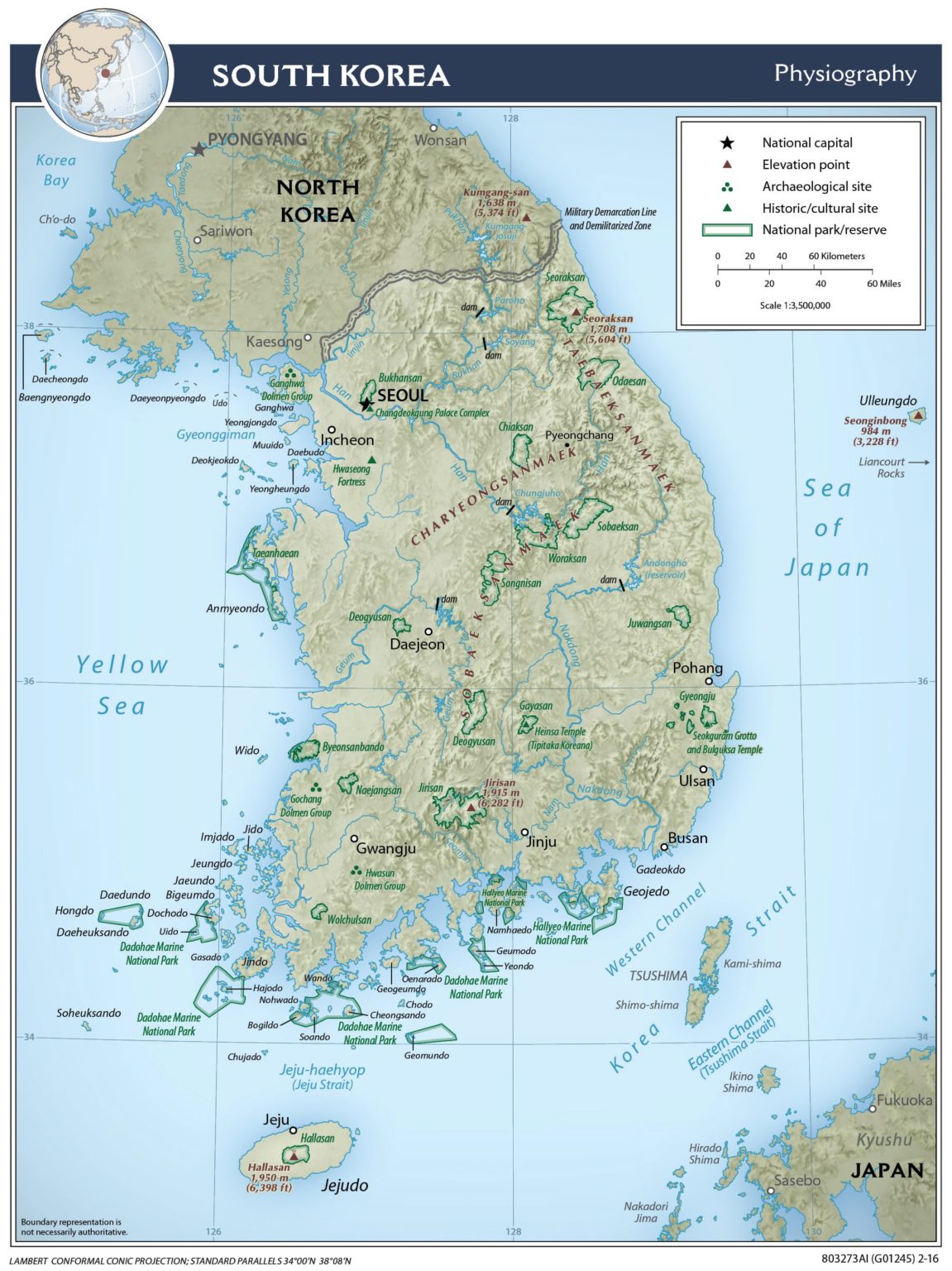


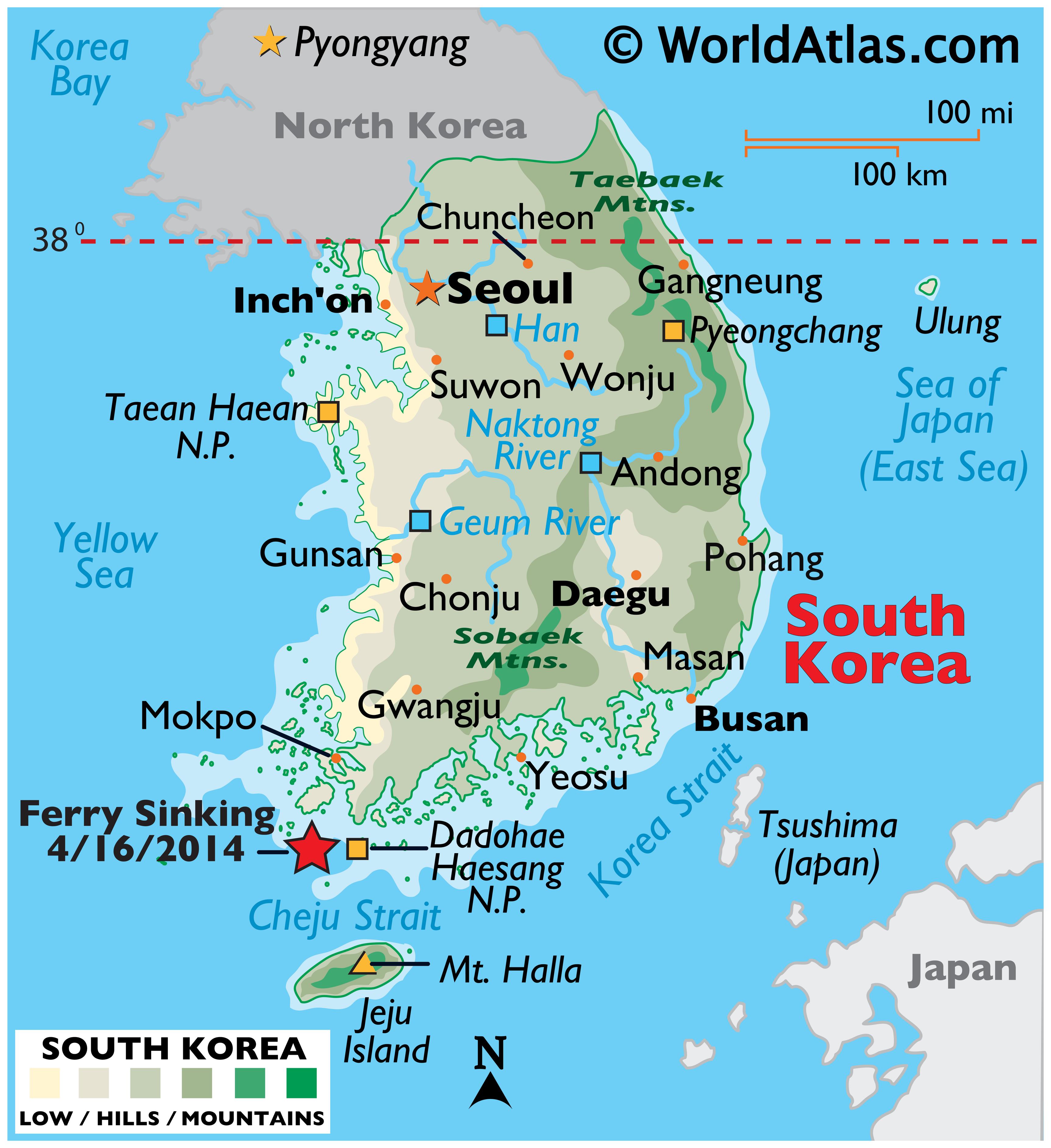
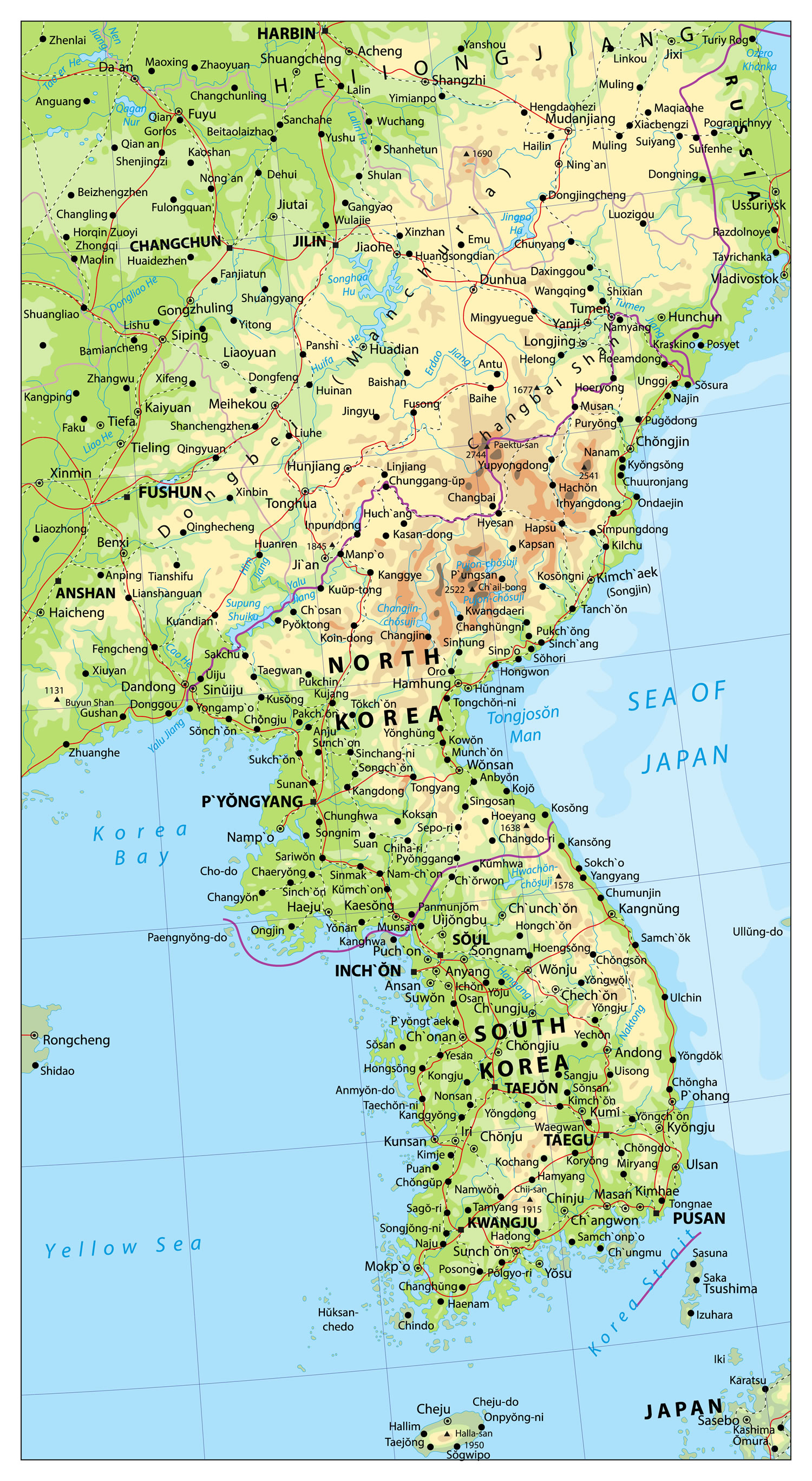



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Korean Peninsula: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of South Korea. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!